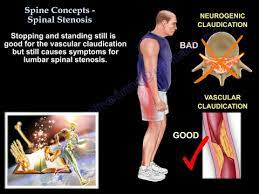
Spinal stenosis, a narrowing of the spaces in your spine, can compress your spinal cord and nerve roots exiting each vertebrae. Age-related changes in your spine is a common cause. Symptoms include back and/or neck pain, and numbness, tingling and weakness in your arms and legs. Treatments are self-care remedies, physical therapy, medications, injections and surgery.
Where does spinal stenosis occur?
Spinal stenosis can occur anywhere along the spine but most commonly occurs in two areas:
- Lower back (lumbar canal stenosis).
- Neck (cervical spinal stenosis).
Who gets spinal stenosis?
Spinal stenosis can develop in anyone but is most common in men and women over the age of 50. Younger people who are born with a narrow spinal canal can also have spinal stenosis. Other conditions that affect the spine, such as scoliosis, or injury to the spine can put you at risk for developing spinal stenosis.
What causes spinal stenosis?
Spinal stenosis has many causes. What they share in common is that they change the structure of the spine, causing a narrowing of the space around your spinal cord and nerves roots that exit through the spine. The spinal cord and/or nerve roots become compressed or pinched, which causes symptoms, such as low back pain and sciatica.
The causes of spinal stenosis include:
- Bone overgrowth/arthritic spurs: Osteoarthritis is the “wear and tear” condition that breaks down cartilage in your joints, including your spine. Cartilage is the protective covering of joints. As cartilage wears away, the bones begin to rub against each other. Your body responds by growing new bone. Bone spurs, or an overgrowth of bone, commonly occurs. Bone spurs on the vertebrae extend into the spinal canal, narrowing the space and pinching nerves in the spine. Paget’s disease of the bone also can also cause on overgrowth of bone in the spine, compressing the nerves.
- Bulging disks/herniated disk: Between each vertebrae is a flat, round cushioning pad (vertebral disk) that acts as shock absorbers along the spine. Age-related drying out and flattening of vertebral disks and cracking in the outer edge of the disks cause the gel-like center of these disks to break through a weak or torn outer layer. The bulging disk then press on the nerves near the disk.